Pioneers of Digital Innovation
Your Vision, Empowered by
Our Expertise
Years of Expertise in Software Development and AI Solutions
Your Vision, Our Expertise
At Pixel Tech, we transform your vision into reality with innovative, AI-driven solutions. With extensive experience in software development, we create custom applications and digital platforms designed to help businesses thrive in today’s tech-driven world.
We specialize in AI integration, mobile app development, and cloud solutions, delivering projects that align with your unique goals. Our focus on cutting-edge technology and quality enables us to support businesses across industries, from startups to large enterprises.
Pixel Tech Services
Why Choose Pixel Tech
Pixel Tech is a leading software development company focused on delivering cutting-edge and customized tech solutions.



Pay After Completion
We only take payment after deliverables are met, ensuring complete customer satisfaction.
Trusted by Brands
Our proven record includes successful projects with Thomson Reuters, Deloitte, HPCL, and SBI.
Rapid, Precise Turnarounds
We deliver high-quality projects ahead of schedule for quicker market entry.
Personalized, Professional Service
Get startup-level attention with enterprise-level reliability, security and expertise.
Comprehensive Solutions
From custom development to digital marketing, we cover all your needs with innovative AI/ML technologies.
Ongoing Support & Scalability
Our solutions evolve with your business, ensuring growth and adaptability with post-development support.

What People Say About Pixel Tech
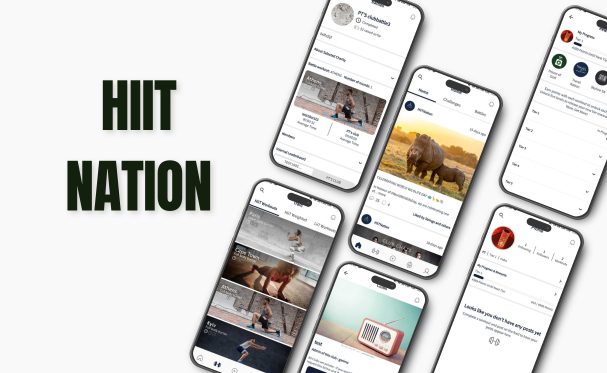
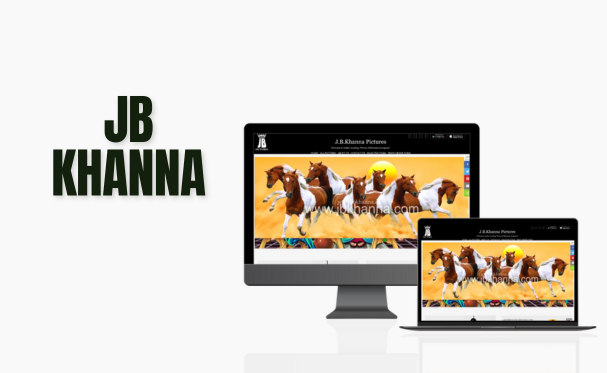
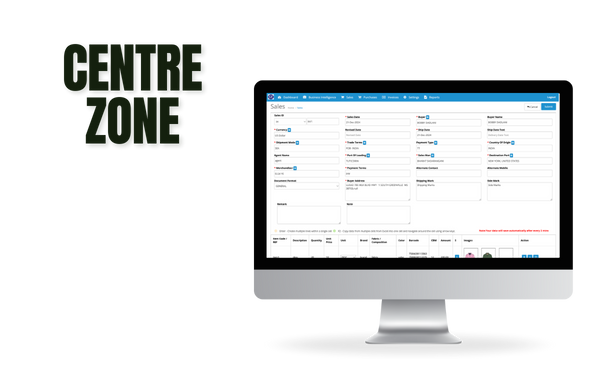
Let’s Explore Our Latest Case Studies
Let's Connect
To discuss your vision
Our Clientele
Cutting-edge Tools That Drive Performance
Innovation
We constantly push boundaries to create cutting-edge software solutions that drive success for our clients. Our innovation is fueled by curiosity and creativity.
Client-Centricity
Every solution we build is tailored to the specific needs of our clients. Their success is our priority, and we are dedicated to going above and beyond in delivering value
Integrity
We believe in honest communication, transparency, and delivering on our promises. We uphold the highest standards in every project we undertake.
Collaboration
Great technology is built through teamwork. We collaborate with our clients and within our teams to bring diverse perspectives to every project.
Quality
Our commitment to delivering high-quality products is unwavering. We ensure that our solutions are efficient, reliable, and built with precision.
Adaptability
The tech landscape is ever-changing, and so are we. We stay agile, embrace change, and continuously learn to keep up with industry trends and client needs.
Sustainability
We strive to build solutions that are not only innovative but also scalable and sustainable for the long term, minimizing tech debt and maximizing longevity.
Excellence
Excellence is at the heart of everything we do. We strive to exceed expectations by delivering exceptional results, maintaining attention to detail, and consistently raising the bar for performance.
Accountability
We take ownership of our actions and deliverables. By holding ourselves accountable, we ensure trust, reliability, and success in every project we undertake.
Next-Gen Digital Solutions For The Enterprises Of Tomorrow
FInTech
Meet the demands of modern customers in speed and security with scalable financial technology
Education
Engaging apps that facilitate learning, adhere to curriculum, and fun for children & Adults
Market Research & Business Intelligence
Empower your potential customers with seamless access to insights, making data-driven decisions effortless through fully integrated digital market research solutions.
Logistics & Delivery
Provide your potential customers with a hassle-free logistics experience, making shipping and tracking as smooth as possible with fully integrated digital solutions.
Food Delivery
Drive your potential customers into a comfort zone where ordering online food becomes a cakewalk with complete digital synced solutions in food delivery
Manufacturing & Productivity
Using enterprise mobility solutions, businesses have tremendous opportunities to modernize their operations to defeat challenges, boost productivity, enrich customer services and earn more revenue
Entertainment
We all know how much entertainment important in our life or in the weekend to burn out our stress, let's give your user the best experience to take their stress out and give them a fresh mind to continue their daily routine again
Real Estate
When it comes to give convenient services to your customers to sell, buy or rent properties, with Real Estate App Development Solutions, you can accomplish all purposes to amplify your business in a contemporary way.
Fitness
All fitness freaks want a great instructor who can guide them better and track their daily activities. let's make fitness enthusiast's experience more energetic by taking your business online
Key AI Capabilities
At Pixel Tech, we specialize in AI-driven solutions that empower businesses to automate processes, make smarter decisions, and enhance user experiences. Our AI expertise spans across various domains, ensuring we offer tailored solutions that fit your business needs perfectly.